
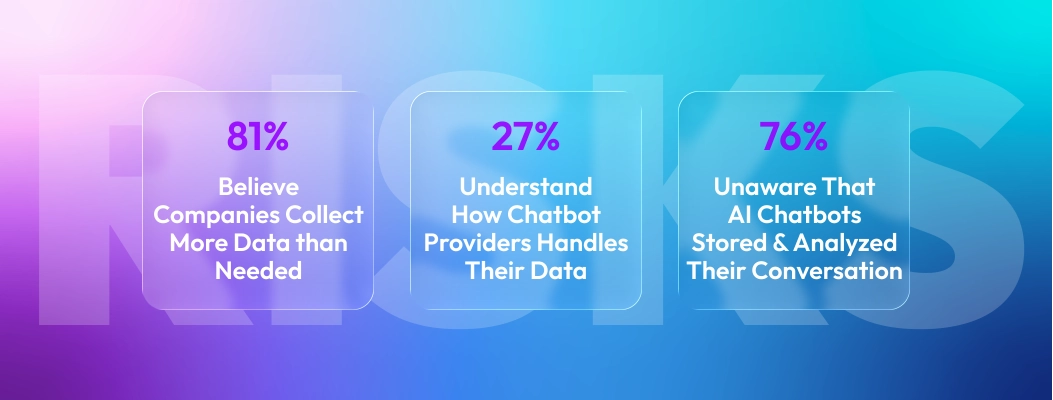
A major misunderstanding is that chatbots only store messages. In reality, many collect device identifiers, browsing activity, contact information, payment data, and behavioral tracking. This makes LLM data training privacy and chatbot data anonymization essential.
Key Statistics
A Surfshark analysis comparing ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Copilot, Meta AI, and 12 other leading apps found:
-
Many AI chatbots collect more personal data than social media apps
-
Several collect precise location, advertising IDs, and usage tracking
An analysis of AI input data found 27.4% of all content fed into chatbots contained sensitive information, including passwords, addresses, and financial details. That’s a 156% increase year-over-year.
Deloitte reported that 91% of enterprises using AI systems share customer data with third parties, increasing the risk of leaks and loss of control.
Many businesses assume chatbots delete or mask conversations, but most LLM-powered bots store chat history to improve their model training. This means customer messages can enter the model’s training data if businesses don’t enable privacy configurations, especially when using generative AI tools for automation.
What This Means for Business Owners
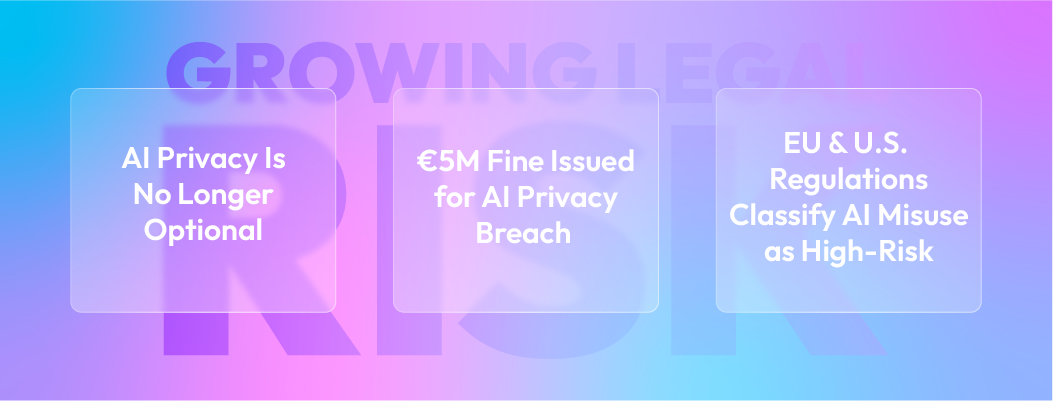
If your chatbot collects personal data, you are responsible under GDPR, CCPA, PDPA, and other global privacy laws. Even if a vendor built the chatbot, your business is accountable for data compliance and must adopt Zero-Trust Security and a Secure AI Framework. Recent actions like the third-party AI chatbots ban in certain regions highlight the growing regulatory scrutiny.






Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
By submitting, you agree to receive helpful messages from Chatboq about your request. We do not sell data.