Emerging worldwide rules for AI assistants are appearing to govern how these programs gather details, create replies, and safeguard patrons from dangers to privacy and well-being. Authorities are establishing tighter guidelines for agreement, clarity, and reliable AI functioning as these conversational tools gain traction in client support and online sales. The goal of this legislation is to encourage businesses to implement artificial intelligence ethically, while mitigating false information, prejudice, and security vulnerabilities.
European Union: AI Act and GDPR

The EU AI Act classifies AI systems by risk and requires transparency, ethical use, and user safeguards.
Chatbots used for customer persuasion, support, and personalization may face requirements such as:
-
Clear disclosures that users are speaking with AI
-
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIA)
-
Human oversight
-
Accurate response monitoring
Under GDPR, businesses must obtain user consent before data processing. Non-compliance can result in fines up to €20 million or 4% of global revenue.
The EU is also readying further rules under the Digital Services Act, Digital Markets Act, and the forthcoming ePrivacy Regulation, which enhance clarity and safeguards for online information. Certain enterprises might also have to satisfy SOC 2 conformity benchmarks for information protection.
United States: FTC & AI Scrutiny

The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has warned companies that AI-powered tools must not:
In 2024, the FTC issued enforcement guidance directing AI companies to train models responsibly and avoid deceptive chatbot practices. Organizations offering chatbot development services must ensure their solutions meet these federal standards. Anticipations of AI hazards are increasingly pointing toward the NIST AI Risk Management Framework for controls at the system level.
Philippines: Data Privacy Act & NPC Oversight
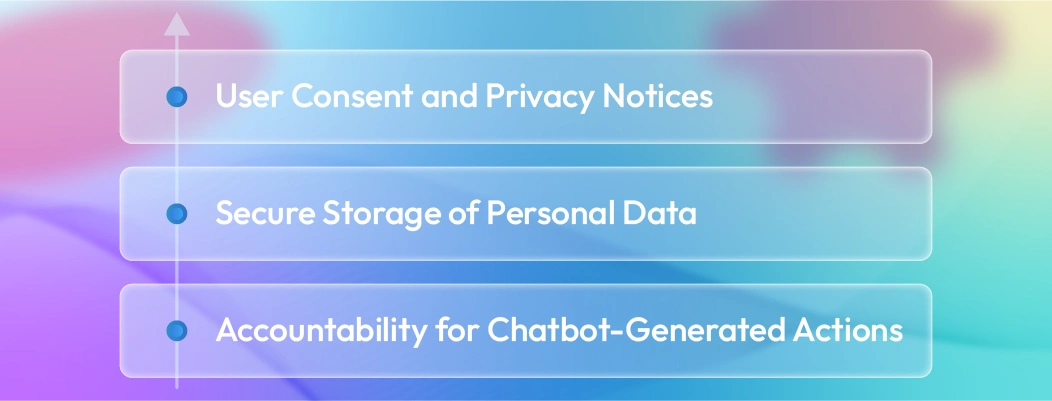
The Philippines’ Data Privacy Act of 2012 applies to e-commerce chatbots collecting customer data.
The National Privacy Commission requires:
-
User consent and privacy notices
-
Secure storage of personal data
-
Accountability for chatbot-generated actions
Retail and fintech platforms have begun conducting Data Privacy Impact Assessments before deploying AI assistants.
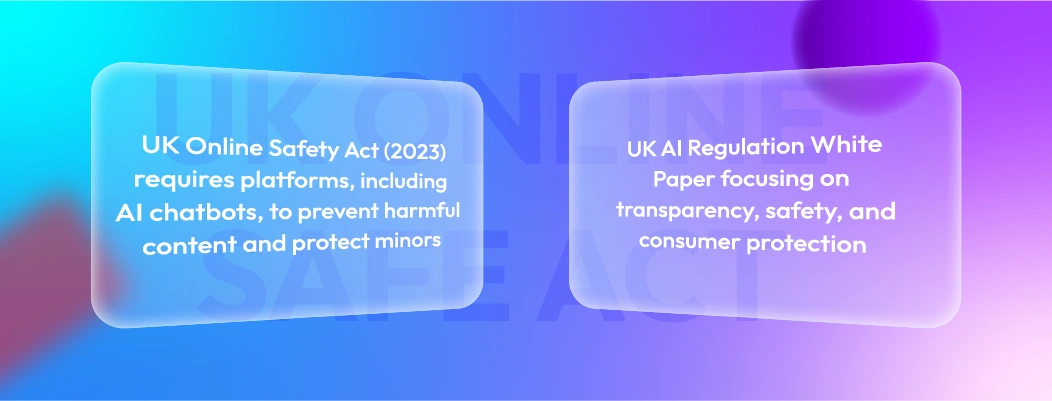
United Kingdom: UK Online Safety Act
-
The UK Online Safety Act (2023) requires platforms, including AI chatbots, to prevent harmful content and protect minors.
-
The government also released the UK AI Regulation White Paper, focusing on transparency, safety, and consumer protection.
-
In situations where AI risks are substantial, promoting transparency through Explainable AI and human-in-the-loop oversight is being advocated.
Canada: AIDA and PIPEDA

-
The proposed Artificial Intelligence and Data Act (AIDA) mandates safe AI deployment, proper data handling, and transparency for AI chatbots.
-
Canada’s PIPEDA privacy law already regulates data collection and automated decision-making.
-
Protections for cross-border data transfer and vendor risk assessments are becoming more and more necessary.
Australia: Privacy ACT AI Ethics Framework

-
The Australian Privacy Act and AI Ethics Framework require disclosure, consent, and responsible use of automated decision-making tools like chatbots.
-
The government has recommended tighter rules to stop AI misinformation and privacy abuse.
-
Security guardrails and vulnerability assessments are increasingly deemed crucial for putting AI systems into use.
Singapore: PDPA

-
Singapore’s AI Governance Framework and Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) regulate customer data used in AI chatbots.
-
Businesses must ensure transparency, explainability, and human fallback options.
-
Data localization guidelines could be relevant based on the nature of the information managed.
India: Digital Personal Data Protection Act

-
India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act (2023) regulates data storage, consent, and AI-driven communication.
-
The government is also drafting AI safety guidelines covering chatbot outputs, misinformation, and bias.
-
Exploring red-teaming alongside algorithmic impact assessments for enhanced scrutiny.
China: Generative AI Provisions

-
China has introduced some of the world’s strictest AI regulations, including:
-
Chatbots must avoid misinformation, label AI content, and keep user data within China unless approved.
-
TLS 1.3, along with AES-256 encryption, is frequently advised for safeguarding chatbot exchanges.
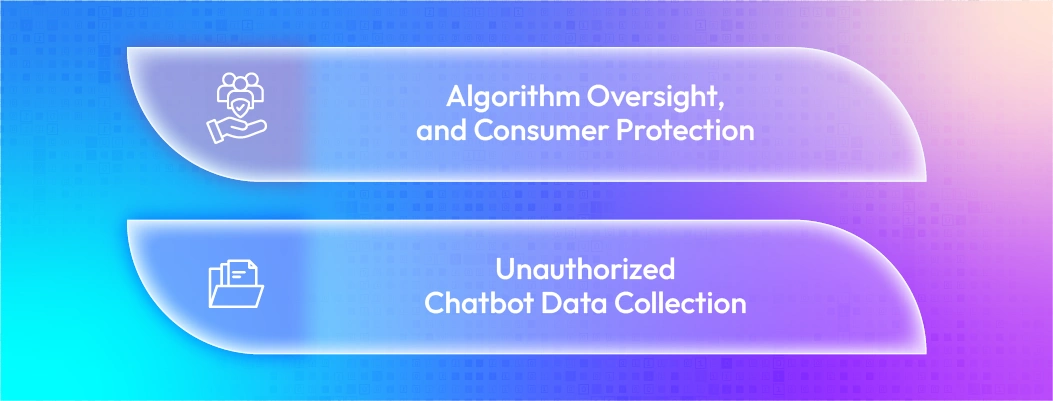
South Korea: AI Basic Act and PIPA
-
Working on the AI Basic Act, which includes transparency, algorithm oversight, and consumer protection.
-
The existing Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA) restricts unauthorized chatbot data collection.
-
Governing AI governance frameworks, encompassing various fields, stress careful implementation.
Japan: APPI Privacy Law

-
Japan supports “safe and trustworthy AI,” with rules under discussion for chatbot transparency and content labeling.
-
The APPI privacy law also applies to chatbot data handling.
-
The right to object and right to data portability are components of user safeguards.
Brazil: Brazil AI Bill and LGPD

-
Draft legislation known as the Brazil AI Bill (PL 2338/2023) proposes regulation over AI safety, bias, and data privacy.
-
Brazil already enforces strict data laws under the LGPD (Brazil’s GDPR equivalent).
-
The right to withdraw consent is gaining significance as enterprises embrace extensive automation.
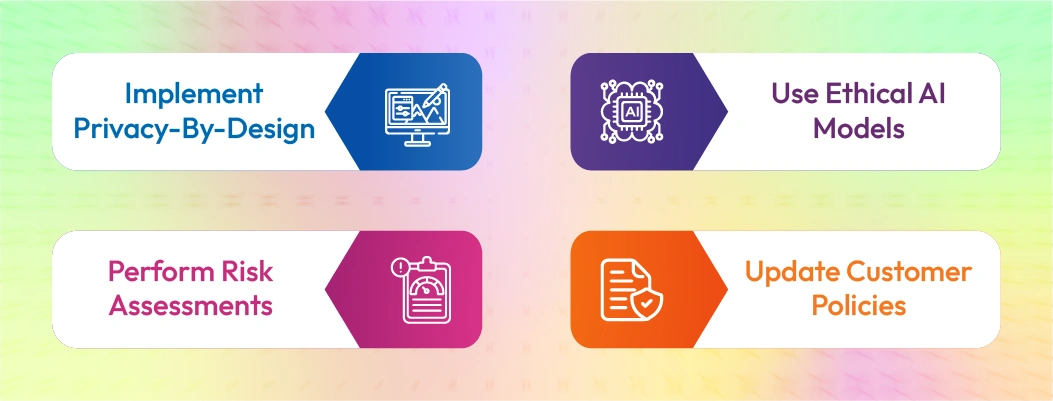
AI Chatbot Compliance Risks Businesses Should Know
Even trusted platforms like OpenAI, Amazon Web Services, and Google DeepMind continue updating safety policies to meet global standards.
Major risks include:
1. Data Privacy Violations

-
Collecting personal data without consent
-
Storing unencrypted chats
-
Third-party data sharing without disclosure
AES-256 encryption and TLS 1.3 are highly advised for lessening these dangers.
2. Biased or Harmful Responses

AI models trained on public data can produce discriminatory or unsafe outputs. The World Economic Forum reports 52% of users worry about AI misinformation. Understanding the risks and disadvantages of chatbots helps businesses prepare adequate safeguards against biased outputs.
3. Lack of Transparency
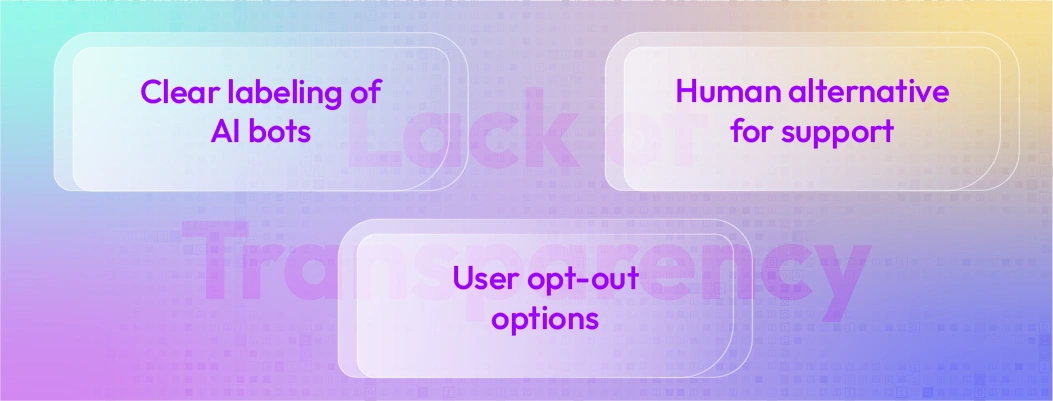
Many countries now require:
4. Cybersecurity Risks

Chatbots can be exploited to:
Recent concerns about platforms like Amazon blocking AI shopping bots highlight the importance of security in automated systems.



















Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
By submitting, you agree to receive helpful messages from Chatboq about your request. We do not sell data.